GPU – Graphics Processing Unit – a hardware processor with many parallel elements for computing the aspects of a player’s surroundings in a video game or the appearace of a building or scene in a picture or video. Such processors have found a role in Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) applications where billions of repetitive calaculations need to be carried out. They are better at this than standard x86 general purpose processors.

[From a Google doc] A modern ML GPU (e.g. H100, B200) is basically a bunch of compute cores that specialize in matrix multiplication (called Streaming Multiprocessors or SMs) connected to a stick of fast memory (called HBM). Here’s a diagram:
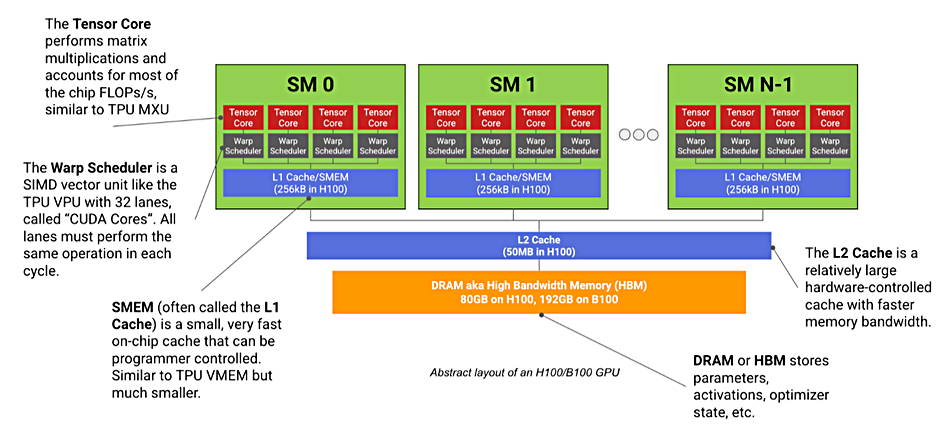
Each SM, like a TPU’s Tensor Core, has a dedicated matrix multiplication core (unfortunately also called a Tensor Core), a vector arithmetic unit (called a Warp Scheduler), and a fast on-chip cache (called SMEM). Unlike a TPU, which has at most 2 independent “Tensor Cores”, a modern GPU has more than 100 SMs (132 on an H100). Each of these SMs is much less powerful than a TPU Tensor Core but the system overall is more flexible. Eac